Novelty of the project
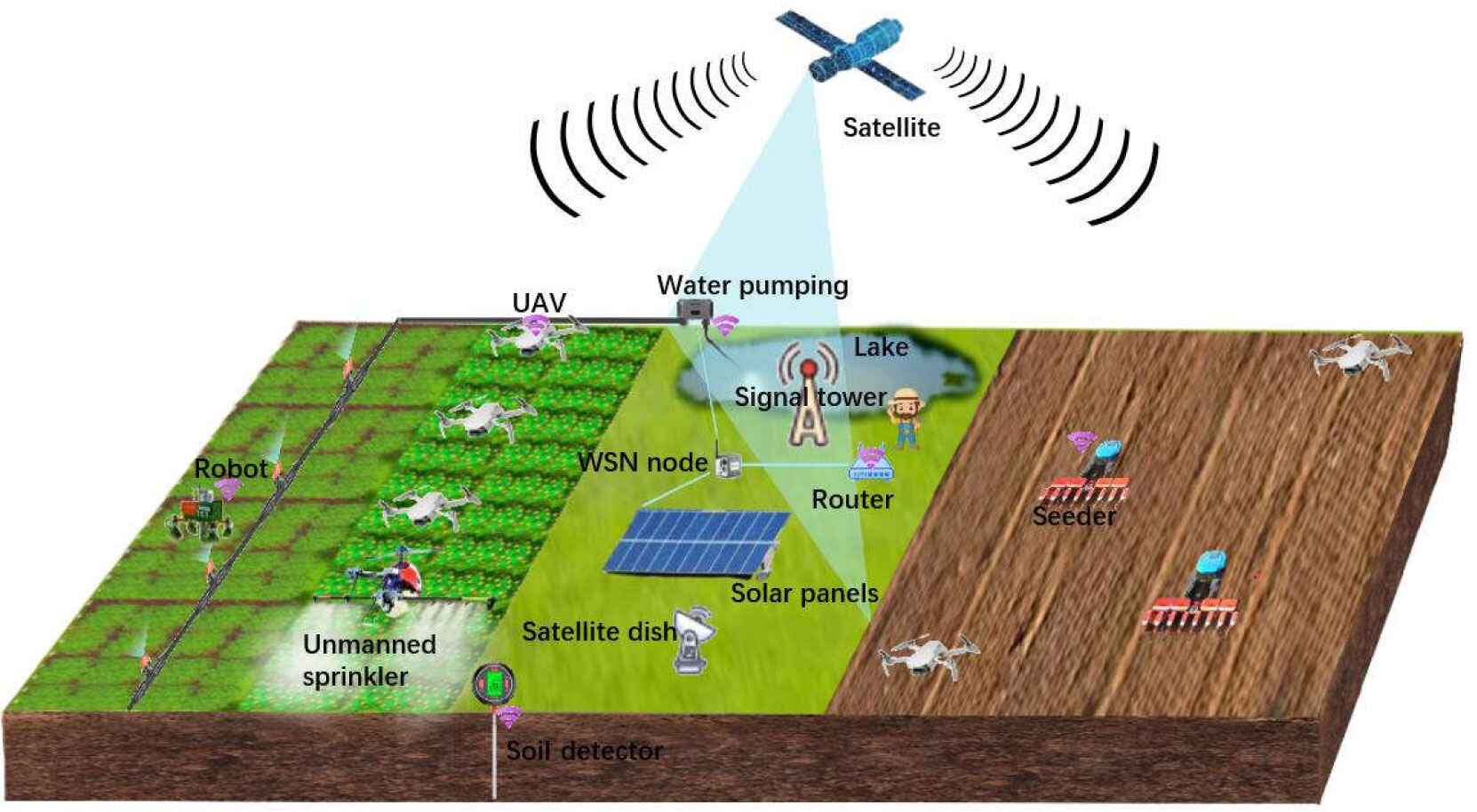
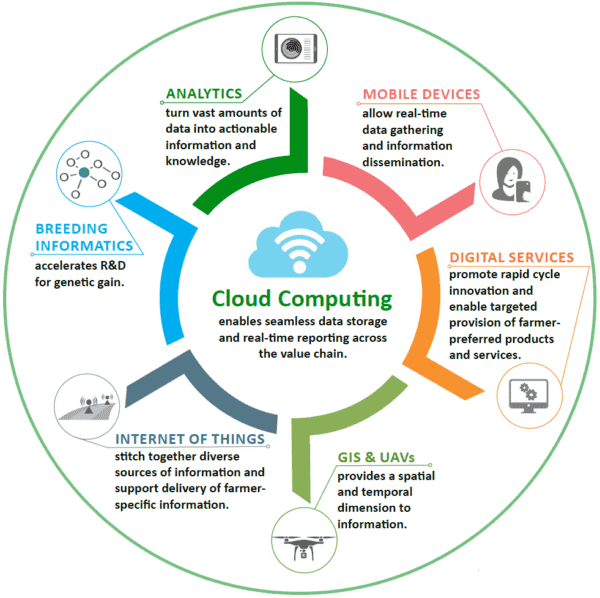
The proposed project combines emerging technologies AR/VR Drone, Robotics, IoT blockchain, and object
detection CNN, to address critical challenges in the agriculture sector, namely seed traceability, farm
implement renting and lending, and precision agriculture. The proposed project is unique in the following
ways:
• Integrated Technological Solutions: The project amalgamates a
diverse range of cutting-edge technologies such as AI/ML, IoT, GIS, drones, robotics, AR/VR, and blockchain.
This integration offers a comprehensive suite of tools and solutions tailored to address multifaceted
challenges in agriculture.
• Empowerment through Collaborative Platforms: The establishment of
kiosk-based centers and collaborative platforms fosters a culture of knowledge-sharing, peer learning, and
community engagement. This collaborative ecosystem facilitates the exchange of ideas, best practices, and
innovation among farmers and rural communities, empowering them with collective knowledge.
• Customized Capacity Building: The focus on capacity-building
programs specifically designed for Self Help Groups (SHGs) ensures targeted learning experiences, equipping
them with essential skills to leverage digital tools effectively. These programs are curated to suit the needs
and contexts of SHGs, fostering inclusivity and personalized development.
• Innovative Pest Management Solutions: The utilization of AI/ML for
insect and pest management, coupled with drone and robotics-based solutions, offers a novel approach to
address crop damage. These technologies enable precise, efficient, and sustainable pest control measures,
minimizing the reliance on conventional chemical-based solutions.
• Transparent Supply Chain and Record-Keeping: The project introduces
a supply chain solution model coupled with transparent and decentralized record-keeping systems. This
innovation ensures transparency, fairness, and traceability throughout the supply chain, providing farmers
with fair market access and consumers with reliable product origins.
• Advanced Precision Agriculture Techniques: The incorporation of
IoT-enabled smart sensors and devices for precision agriculture, including smart irrigation systems, promotes
resource-efficient farming practices. These technologies enable optimized water usage, real-time monitoring,
and data-driven decision-making for enhanced productivity.
• Immersive Learning and Support: The adoption of augmented reality
(AR) and virtual reality (VR) provides farmers with immersive learning experiences. This novel approach
enhances training and support mechanisms, enabling SHGs to grasp complex concepts and agricultural practices
in a more interactive and engaging manner.
• Financial Inclusion and Market Access: The emphasis on financial
inclusion through digital financial services and secure market linkages enables SHGs to access credit
facilities and market opportunities, fostering economic viability and growth.
• Data-Driven Decision Making: Leveraging Geo-Tagged Based farm
digitization and business intelligence solutions enables farmers to make informed decisions through data
analytics, leading to optimized crop management and increased yields.
Benefits
The benefits accruing to the target groups, primarily Scheduled Tribe (ST) farmers and smallholder groups,
from the Digital Agri Village project are diverse and impactful.
Increased Agricultural Productivity and Income
Generation:
• Enhanced income generation opportunities for ST farmers due to higher productivity, leading to improved
livelihoods and economic stability.
Enhanced Access to Information and Technology:
• Empowerment of ST farmers with updated information, technological literacy, and skill enhancement for
efficient farm management.
Fair Market Access and Transparent Pricing:
• ST farmers gain access to wider markets, bypassing middlemen, ensuring fair pricing, and reducing
exploitation in the supply chain.
Improved Resilience and Climate Adaptation:
• Increased resilience against climate risks, minimizing crop failures, and economic losses for ST farmers due
to better adaptation strategies.
Community Empowerment and Collaborative Learning:
• Strengthened community engagement, shared learning, and collective decision making among ST farmers,
fostering community empowerment and cohesion.
Healthier and Sustainable Farming Practices:
• Improved health outcomes for ST farmers and consumers due to reduced chemical exposure and access to
healthier, sustainably grown produce.